Lalas
Star
- Joined
- Nov 8, 2022
- Messages
- 2,129
What should I throw away? Putin's daughter?Dump it over. Can it right itself? If not, is useless.
(Because the last time, we talked about her...)
What should I throw away? Putin's daughter?Dump it over. Can it right itself? If not, is useless.







 mniipu.org
mniipu.org
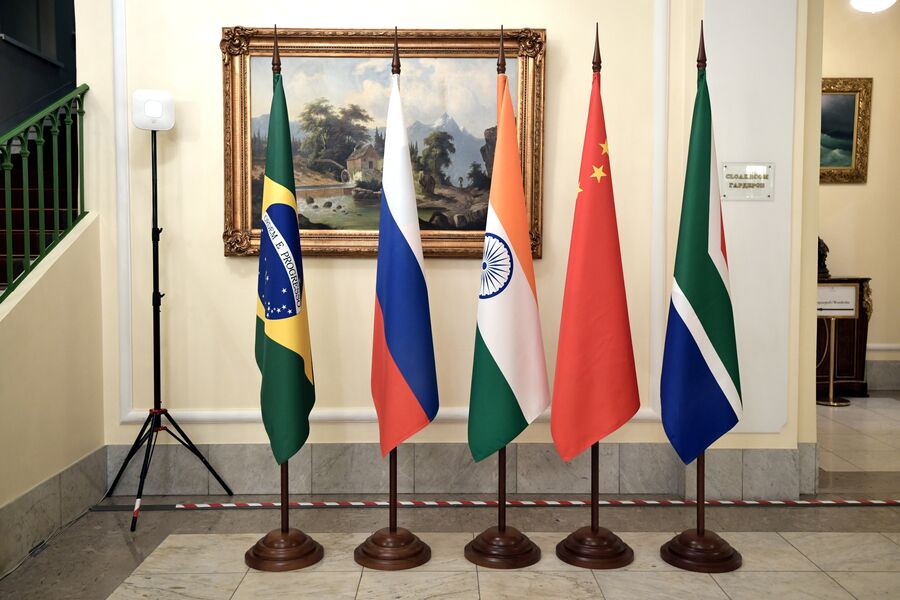
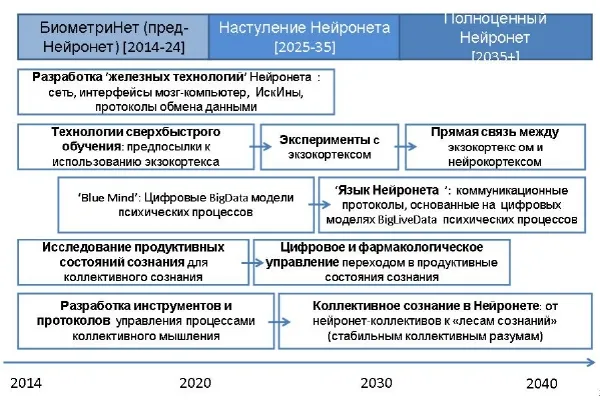
At the GLOBALISTICS 2023 Congress, a report by MSU scientists "Rethinking the Limits to Growth" was presented
...
The report, edited by V.A. Sadovnichy, A.A. Akaev, I.V. Ilyin, S.Y. Malkov, L.E. Grinin, and A.V. Korotaev, was prepared in 2020–2022 as part of the development program of the Interdisciplinary Scientific and Educational School of Moscow State University "Mathematical Methods for the Analysis of Complex Systems" and the implementation of a grant from the Russian Science Foundation.*


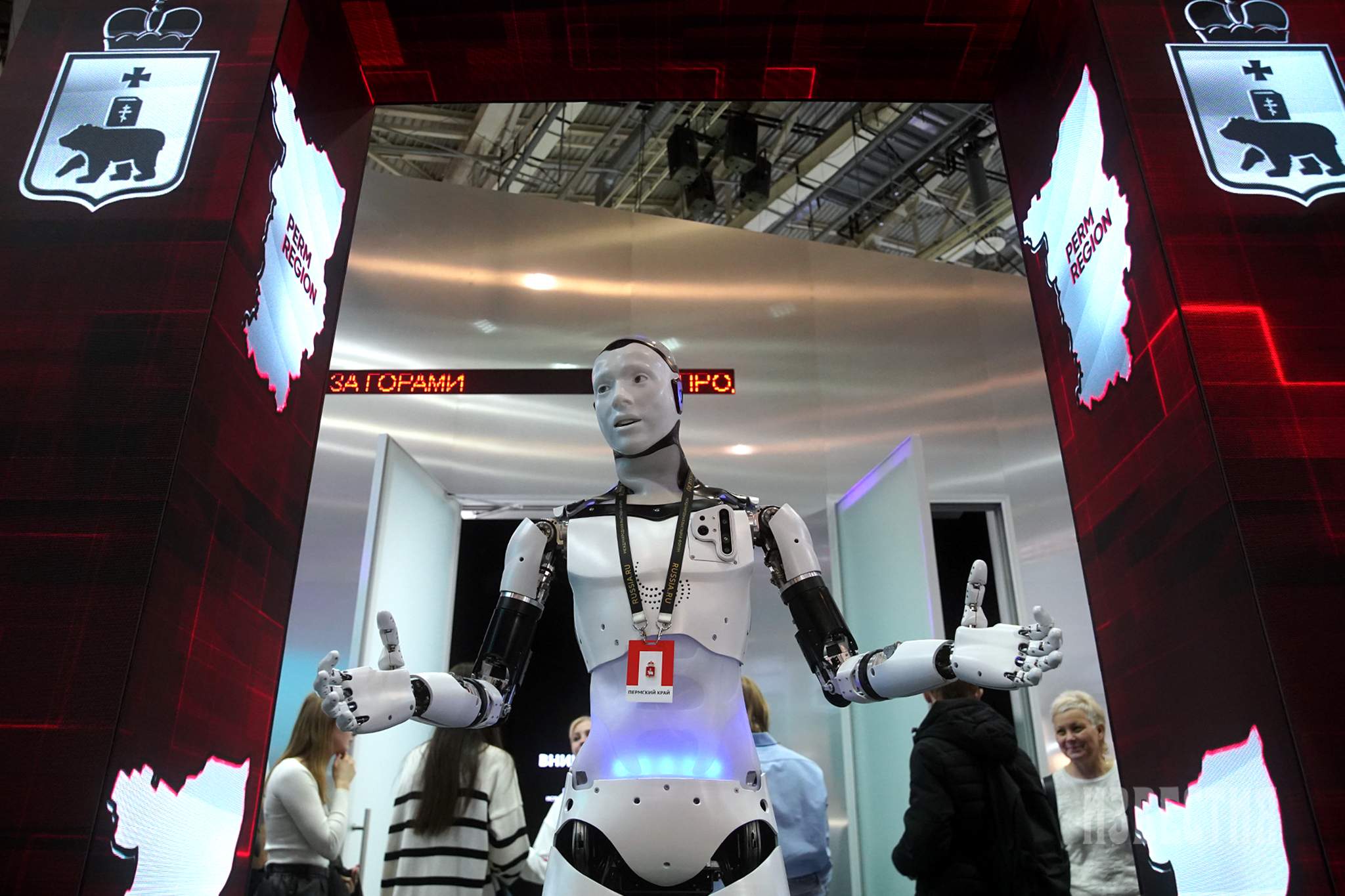
The robot waiter and robot cat thing. If I run into one, it's going over.What should I throw away? Putin's daughter?
(Because the last time, we talked about her...)
I agree 100%. Stupid robocat, suck it!The robot waiter and robot cat thing. If I run into one, it's going over.
Then I will kick it.
It it cannot get up, it's useless.
I like watching the videos of people assaulting the robot things.
































/imgs/2023/12/14/16/6272864/c2cacc6be09ff4f9a7c3e8342f9e07fd059b3fb9.jpg)




/imgs/2023/12/20/10/6280821/b6b754b3c3f4742c06ef2956ab57fab246e0fe37.jpg)













 www.eneuro.org
www.eneuro.org


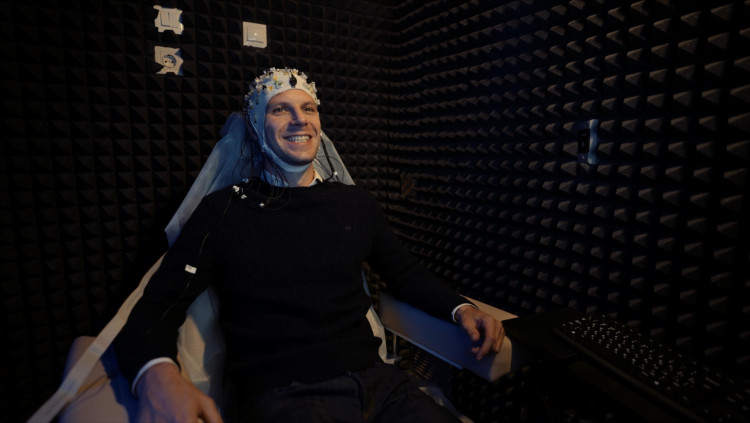
Supervisor: Kaplan Alexander Yakovlevich, Doctor of Biological Sciences









 thepressunited.com
thepressunited.com


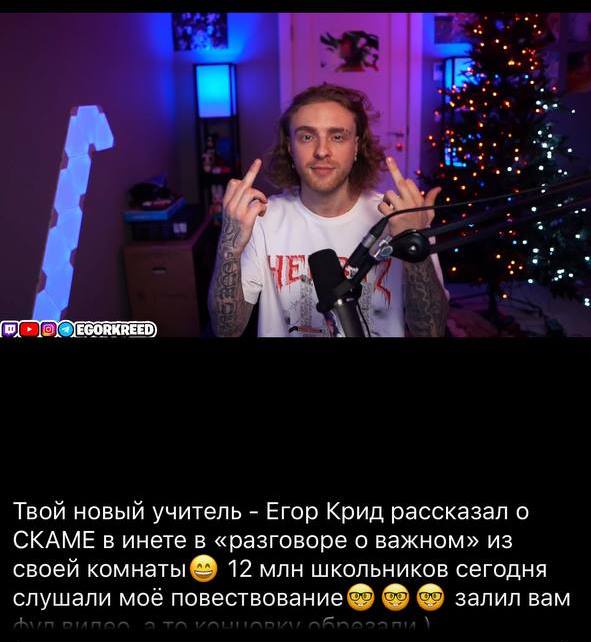






 www.sostav.ru
www.sostav.ru














.jpg)