"The Federal Service for Supervision in the field of consumer protection and human well-being"
ROSPOTREBNADZOR
Rospotrebnadzor is monitoring the epidemiological situation on COVID-19
22.05.2024
Rospotrebnadzor specialists are constantly monitoring the incidence of a new coronavirus infection. After the holidays, there is a previously predicted increase in the incidence of COVID-19, associated with a large number of contacts between people during the holidays.
Monitoring of the circulation of SARS-CoV-2 variants continues throughout the Russian Federation. As before, as in the rest of the world, the Omicron genovariant remains predominant.
Monitoring allows you to identify even single new genovariants. For the entire monitoring period, 178 cases of new FLiRT variants were detected, including KP.2 (3 cases), KP.1.1 (5 cases), KS.1 (170 cases). All of them are no more dangerous than its other varieties.
The symptoms of FLiRT variants are similar to Omicron - fever, cough, sore throat, weakness, headache, muscle aches, loss of taste/smell.
It is important not to neglect preventive measures - wash your hands more often, ventilate rooms, disinfect work surfaces and gadgets, avoid contact with people with signs of disease. And the most important thing is not to self-medicate, but immediately consult a doctor in order to avoid negative consequences for your health.
Russia and Uzbekistan signed an intergovernmental agreement on cooperation in ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population
27.05.2024
On May 27, as part of the state visit of Russian President Vladimir Putin to Uzbekistan, the head of Rospotrebnadzor Anna Popova and the chairman of the Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare and Public Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan Bakhodir Yusupaliyev signed an intergovernmental agreement on cooperation in the field of ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population.
The agreement covers all aspects of cooperation in the field of ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population, including the prevention and monitoring of infectious diseases, the elimination of the harmful effects of environmental factors on humans, ensuring food safety, as well as responding to sanitary and epidemiological emergencies.
The conclusion of the Agreement confirms the commitment of Russia and Uzbekistan to strengthen actively developing cooperation. To date, such interaction is carried out within the framework of 5 joint projects. In Uzbekistan, there are 6 mobile laboratories and 2 mobile clinics donated by Rospotrebnadzor within the framework of such programs, more than 300 specialists of the Republic of Uzbekistan have been trained, 7 joint exercises have been held.
The implementation of the Agreement will deepen bilateral relations between the countries in the field of epidemiology, sanitation and hygiene, and will make it possible to effectively respond to the threats of infections throughout the single Eurasian epidemiological space.
International anti-epidemic exercises started in Saratov
28.05.2024
On May 28, the fifth exercises of the rapid response teams of the CIS member states to sanitary and epidemiological emergencies started on the basis of the Russian Anti-Plague Institute "Microbe" of Rospotrebnadzor in Saratov. The event is held within the framework of the federal project "Sanitary Shield".
More than 70 representatives of specialized organizations from 6 countries - Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, as well as specialists from anti-plague institutes of Rospotrebnadzor take part in the exercises.
Today, the opening of the exercises took place, during which the teams prepared mobile laboratories for work, took samples of environmental objects. In the following days of the exercises, specialists will examine encrypted sample panels, solve epidemiological problems, work out logistics schemes and emergency response skills. A significant part of the exercise will be occupied by the study of encrypted samples using modern molecular genetic methods (PCR and sequencing).
To conduct the exercises, the laboratories of the mobile complex of specialized anti-epidemic teams of the second generation, as well as a mobile indication and monitoring laboratory based on a chassis and a portable mobile laboratory based on a pneumatic frame module are actively involved.
РФ вошла в тройку лидеров по заболеваемости корью в европейском регионе

www.kommersant.ru
30.05.2024
The Russian Federation entered the top three in terms of the incidence of measles in the European region
Russia is among the top three in terms of the number of measles infections among the countries of the European region of the World Health Organization (WHO). The WHO announced this after analyzing the relevant statistics from April 2023 to March 2024. The Russian Federation is ahead only of Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan, and Kyrgyzstan follows directly after our country in this list. The WHO warns that the incidence of measles in the European region continues to grow - the trend is provoked by the problems associated with the coronavirus pandemic. In Rospotrebnadzor, earlier the surge in incidence was associated mainly with the appearance of a large number of unvaccinated citizens arriving just from neighboring countries.
...
Almost half of the reported cases in 2023 were in children under five years old.
This, according to experts, is due to an increase in the number of children who missed routine vaccinations against measles and other vaccine-preventable diseases due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and the slow recovery of vaccination coverage in 2021 and 2022.
...
Kommersant said that from January to September 2023, 8073 cases of measles were detected in Russia - compared to the same period a year earlier, the increase was 28,732% (288 times). This follows from the data of Rospotrebnadzor, which was first noticed by the publication "Medvestnik". Most of the cases (4989 people) are children under 14 years old.
At the same time, the incidence of other vaccine-preventable infections is also increasing.
So, Medvestnik, citing data from Rospotrebnadzor, reported that the incidence of whooping cough in Russia broke a 30-year record - in 2023, the infection was detected in almost 53 thousand people, there were more only in 1993.
...
The increase in the incidence of measles in 2023 in Rospotrebnadzor is explained by "another cyclical rise, traditional for this disease." In a number of regions of the Russian Federation, an increase in the incidence is noted mainly among unvaccinated citizens, including those who arrived from neighboring countries, the press service of the department pointed out. It should be noted that according to the FSB, in 2023, the main influx of labor migrants to Russia occurred at the expense of visitors from Uzbekistan (630,859 people), Tajikistan (349,357), Kyrgyzstan (172,591), Armenia (47,337) and Kazakhstan (34,783). Group foci of the disease during the year were also observed among the "Roma population and religious communities refusing vaccinations." Throughout the country, since April 2023, Rospotrebnadzor has been conducting clean-up immunization - vaccination of unvaccinated and not ill with measles, as well as children and adults vaccinated once.
In Russia, news about quarantine has recently regularly appeared due to the detection of cases of measles in educational institutions.
MEPhI University went further and on May 28, 2024, introduced measures to prevent measles due to the tense epidemiological situation, the university's press service reported. Students who do not have measles vaccinations and do not have the appropriate antibodies were recommended by the university administration to be vaccinated. Students should submit a certificate of vaccination by May 31, otherwise, if the disease is detected at the university, they will be banned from entering the territory of the university for three weeks.
...
Regina Grigorieva, a leading pediatrician, deputy chief physician of the Nearmedic clinic, confirms that the intensity of the incidence of measles in Russia is growing. According to her, this is due not only to migration processes, but also to the growth of the anti-vaccination movement in the country. "The increase in measles is a clear sign of declining immunization coverage. As the number of measles cases continues to grow, active vaccination of both children and adults is needed," Ms. Grigorieva points out.
**
Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (National Research University)

mipt.ru
Get vaccinated against measles!
May 29, 2024
The situation with the incidence of measles remains tense throughout the Russian Federation. Currently, measles has been detected in 44 regions of the country. In the capital, there is also an increase in sporadic morbidity, mainly among citizens who are not vaccinated against the infection. The epidemic situation with the incidence of measles in the Moscow region has also become more complicated.
Taking into account the current epidemiological situation, it is necessary to immunize against measles not only for contact persons, but also for all previously unvaccinated and not sick students and employees of MIPT.
Protect yourself and your loved ones, get vaccinated!
You can get vaccinated in the polyclinic No2 of the DCGB (2nd floor of the MIPT medical center). The vaccine is available in sufficient quantities.

mipt.ru
Future Phystech Students Were Told About New Areas of Study at MIPT
April 14, 2024
..
MIPT today is one of the leading universities in Russia. Over the past few years, significant changes have taken place at MIPT – new laboratories and institutes have been opened: biophysics of the future, quantum technologies and electric propulsion.
The university is constantly working to improve the quality of life of students who spend a significant part of their time on campus. MIPT has serious plans to improve its infrastructure: a new educational and laboratory building, new research centers and institutes are being built on the territory of the future Phystech Valley ISTC.

mipt.ru
Phystech School of Nature-Like, Plasma and Nuclear Technologies named after I.V. Kurchatov
About the Phystech School
The Igor Kurchatov Phystech School of Nature-Like, Plasma and Nuclear Technologies appeared at MIPT in April 2024. It combines several structures: formed on the basis of the Kurchatov Institute, the new Phystech School includes the Institute of Nano-, Bio-, Information, Cognitive, and Social Sciences and Humanities and Technologies, the Department of Plasma Physics and Chemistry, the Department of Modeling of Nuclear Processes and Technologies, the Department of High Energy Physics and the Department of Astrophysics and Quantum Field Theory.
The departments of the institute are a single educational complex that teaches general and special disciplines of the institute, faculty and basic cycles:
Department of NBIC Technologies;
Department of Plasma Physics and Chemistry;
Department of Modeling of Nuclear Processes and Technologies;
Department of High Energy Physics;
Department of Astrophysics and Quantum Field Theory;
Department of Physics and Physical Materials Science;
Department of Mathematics and Mathematical Methods of Physics;
Department of Informatics and Computer Networks;
Department of Humanities.
The staff of the departments are prominent scientists who combine scientific work and teaching. Specialists from the Kurchatov Institute, institutes of the Russian Academy of Sciences, employees of the National Research University MIPT, Lomonosov Moscow State University and other leading universities in Moscow teach at the faculty.
CST Educational Programmes:

mipt.ru
Nature-Like Technologies and Biomimetic Design of Materials and Systems
Joint Department:

mipt.ru
Department of Nano-, Bio-, Information and Cognitive Technologies
The Department of NBIC Technologies was established in June 2010 at the Faculty of Nano-, Bio-, Information and Cognitive Technologies (FNBIC) of MIPT, the basic faculty of the National Research Center "Kurchatov Institute".
The Kurchatov Complex of NBICS Nature-Like Technologies of the National Research Center "Kurchatov Institute" is the educational and scientific base of INBIXT and the Department of NBIC Technologies.
The Kurchatov Complex of NBICS Nature-Like Technologies, focused on interdisciplinary research and development, conducts research in the field of nano-, bio-, information, cognitive, socio-humanitarian sciences and technologies, using X-ray, synchrotron and neutron radiation.
The experimental basis of the complex is megafacilities: a synchrotron radiation source, a neutron source based on the IR-8 reactor (both facilities are equipped with a wide range of analytical and technological stations for work in the field of materials science, nanobiotechnology, and medicine).
The NBICS Center includes state-of-the-art laboratories for high-resolution electron and probe microscopy, polymer materials, genomic and proteomic studies, cognitive sciences, superconductivity, etc.
Programs:

mipt.ru
Convergent Nano-, Bio-, Information and Cognitive Technologies. Master

mipt.ru
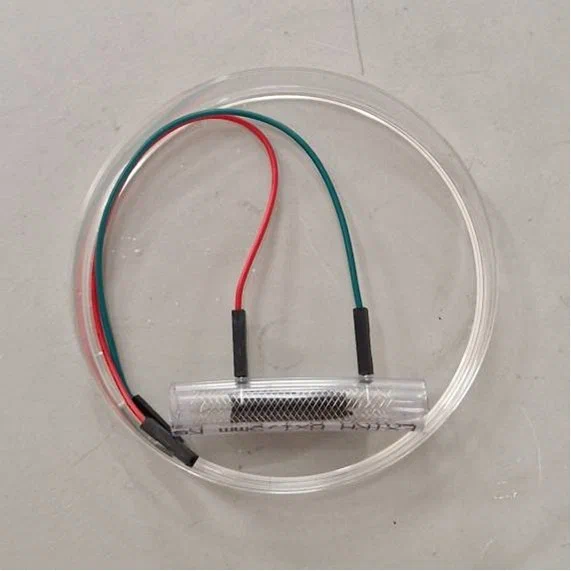
MIPT has created an "eternal" power source for cardiac implants
April 23, 2024
Ekaterina Vakhnitskaya, a master's student at the Kurchatov Phystech School of Nature-Like, Plasma and Nuclear Technologies, has developed an enzyme biofuel cell for implantable medical devices. The proposed model does not require replacement, unlike lithium-ion batteries, which must be rotated every 5-10 years. Surgical medical interventions are traumatic for patients and critically dangerous for the elderly.
An enzymatic biofuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy using biocatalysts. The formation of electrons at the anode occurs due to oxidation by an enzyme. Simply put, the mechanism works by oxidizing glucose. In the development of this device, a stent was used to insert an electrochemical element into the vessel in a minimally invasive way. The installation takes place by angioplasty, i.e. through a puncture in a vein or artery. The stent is inserted into the vessel, and when it hits the right place, it is inflated with a special balloon.
The use of such an element can be fully called a tool for health preservation. The operation to install the device does not involve extensive surgery: the installation is carried out through a stent (a special frame that is placed in the lumen of the coronary vessels of the heart or bile duct, and provides expansion of the area). For comparison: surgery during pacemaker replacement lasts about an hour. The doctor makes a small incision in the skin, the old pacemaker is disconnected from the electrodes and removed from the pocket between the muscles. A new pacemaker is placed in its place and connected to the same electrodes. Then the device is tested and the incision is sutured.
The use of a biofuel cell (BTU) will prevent such surgical interventions to replace the battery, since the mechanism uses glucose from the body as fuel, the concentration of which is kept constant due to homeostasis. Stent implantation completely excludes open surgery. Of the promising safest ways to solve the problem, wireless charging of the device can be singled out, but this will be accompanied by heating of the surrounding tissues, which is not very favorable for the body
said the author of the project, MIPT student Ekaterina Vakhnitskaya.
The enzyme biofuel element will be able to be used by patients who use active implants, as well as people with diabetes mellitus, to power biosensors and other sensors. According to Ekaterina Vakhnitskaya, the development is also useful for the scientific community - the device can act as a model for the creation of other biomedical devices.
A biofuel cell converts the chemical energy of organic substances into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction. It consists of an electrolyte, an anode, and a cathode. The principle of operation of the element is the oxidation of fuel at the anode with the release of electrons and protons. The protons then penetrate through the electrolyte solution to the cathode, and the electrons pass through an external circuit to which a load is applied. The electrons are then transferred to the cathode, where they are used along with free protons to reduce oxygen to water."
explained Ekaterina Vakhnitskaya.
The project "Development of an enzyme biofuel cell integrated into a stent for vascular surgery" became the winner of the UMNIK competition and received a grant of 500 thousand rubles.
Now researcher Ekaterina Vakhnitskaya is working on improving the design of the biofuel cell. In the near future, the MIPT student intends to conduct tests in vitro (in artificial conditions, outside the body or natural environment).
Biofuel Cell (general plan)

mipt.ru
More than 35 million rubles for the education of 94 MIPT students collected a grant competition in 2023
October 6 2023
This year, the Faculty of Applied Mathematics, together with the Phystech Union and the MIPT Alumni Initiatives Center, conducted a traditional campaign to raise funds for the training of talented applicants and students of the Faculty of Applied Mathematics.
The so-called "grant" competition is being held for the 4th time.
The grant allows you to provide a discount on tuition from 50% to 100% for the entire period of the bachelor's degree to an applicant who, for some reason, did not have enough points to pass the threshold. The fadraising campaign also replenishes the budget to pay tuition fees for those students who received grants earlier.
For applicants, a prerequisite for applying for a grant is demonstrated significant success in Olympiads and competitions, talented implemented projects. Grants are awarded based on the results of interviews. For several years now, this practice has shown excellent results. Grant recipients are mainly children from the regions, whose families do not have enough money to pay full tuition fees.
Grantors are initiative and caring graduates of MIPT, as well as alumni companies, where many PhysTech students have historically worked.
In 2023, about 35,000,000 rubles were raised thanks to the fundraising campaign. The Phystech School was traditionally supported by 1C LLC, VTB Bank (PJSC), SberTech, and the MIPT Endowment Fund. The share of financing by companies is 50%. Another 50% of donations came from individuals.
..
From the motivation letters of the participants:
I see myself as a student of the Faculty of Applied Mathematics and Mathematics, because I have learned to overcome any difficulties and bring things to an end, which is confirmed by the graduation from the Central Children's School of International Education and Yandex Lyceum (with honors). I am especially proud that I was able to graduate from Lyceum++, since the training was difficult and intensive, mostly independent. The most important skill I learned during my studies is that I learned to learn. This skill helped me in passing to the final stage of the Higher School of Education in Computer Science, since I prepared on my own. I am sure that this skill will help me in my studies at the Faculty of Applied Mathematics.
I believe that I will be able to get the strongest fundamental education in the field of mathematics, computer science, and physics by studying at the Faculty of Applied Mathematics. Most of all, I am attracted by the opportunity to apply my knowledge of mathematics, physics, and computer science to the field of neural implants in the future. I consider this area to be one of the most promising at the moment, both in terms of research and in terms of commerce. The achievements of Synchron, whose neural implant has successfully passed clinical trials, Braingate and Neuralink, founded by Elon Musk, make it clear that the intersection of engineering and biology in the 21st century will have the same importance as physics and engineering in the 20th.

mipt.ru
Scientists have taught nanoparticles to outgrow themselves electromagnetically
August 15 2023
An international team of physicists has shown that a certain shape allows nanoparticles to be electromagnetically larger than their geometric dimensions. The discovered effect will help in the creation of biological sensors, materials for solar cells and elements of optical quantum computers. The study is published in the journal Nature Communications.
The scattering of light by small particles plays a central role in a myriad of fields. Here, the authors demonstrate a super dipole resonance that arises when two resonant modes of a small particle interfere, overcoming a widely accepted limitation to the cross section.

www.nature.com
..
The study was supported by the Federal Academic Leadership Program "Priority 2030"

mipt.ru
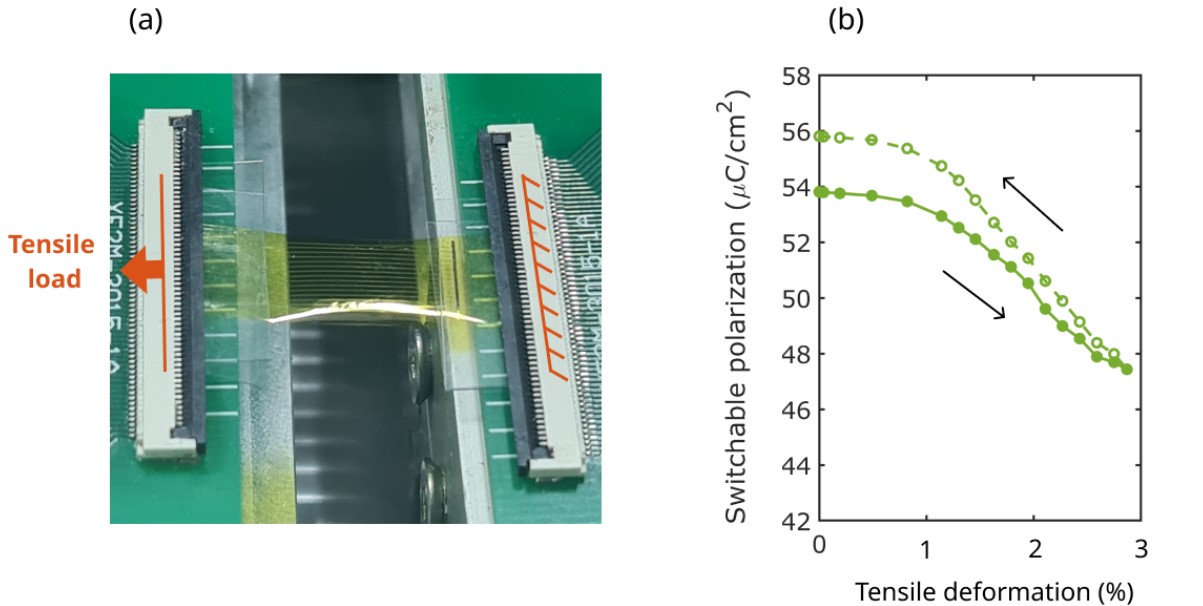
MIPT scientists have created an ultra-flexible biocompatible flash drive
March 14
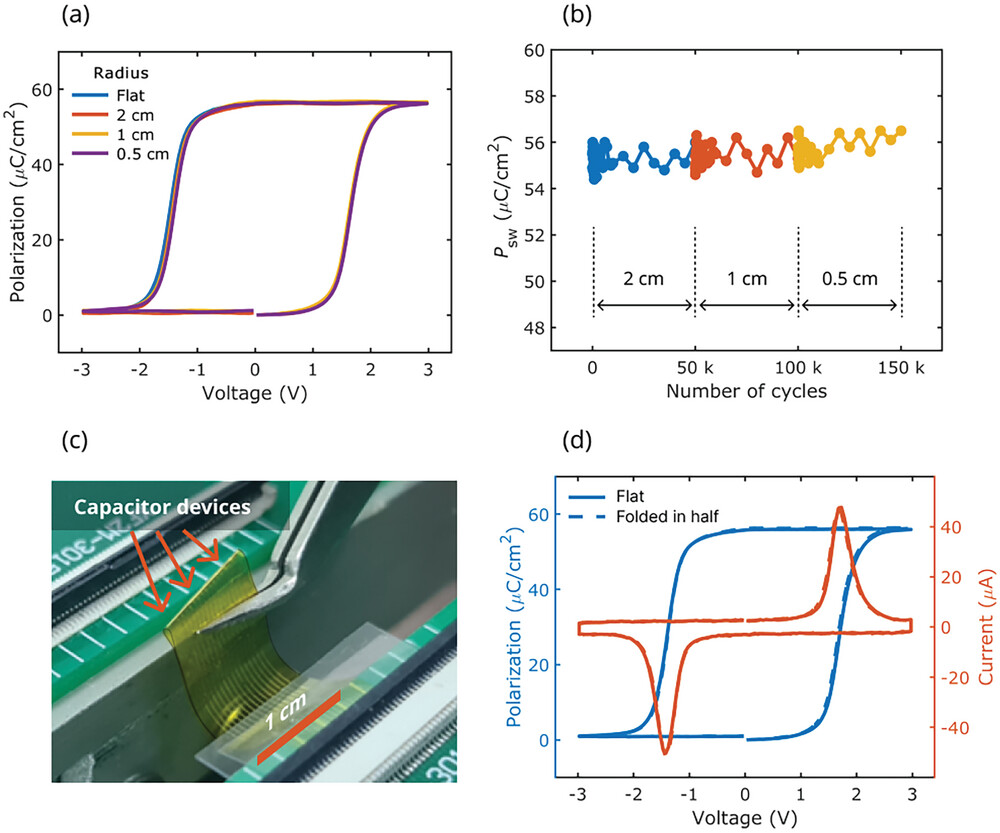
Researchers from the Institute of Quantum Technologies of MIPT have created an ultra-flexible and stretchable ferroelectric memory on a biocompatible platform. They developed a technology for the production of film memory, a stand for testing its properties and theoretically confirmed the results of experimental tests. The resulting "flash drive" with a thickness of only 30 micrometers can withstand 150,000 bending cycles and a tensile load of one and a half kilograms, without losing its ferroelectric properties, and can be used to create flexible medical electronics. The study is published in the journal Advanced Electronic Materials.
Flexible memory is needed in a variety of applications: bendable displays, e-paper, e-textiles. Devices structurally similar to flexible memory can be used in green energy devices to convert mechanical deformations into electrical energy and recharge batteries.
Its use in healthcare is very promising. Smart wearable sensors could be attached to a person's skin to read in real time, for example, blood pressure, pulse, body temperature - and immediately record and process them. Or it would be possible to make "smart" implants. For example, neural implants that would contain microcontrollers and non-volatile memory. Such devices can help in the treatment of neurological diseases associated with brain disorders: epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, severe clinical depression and others.
Memory devices based on ferroelectric materials are non-volatile, allow fast reading and writing of data, have a long data rewrite resource, low power consumption and compact dimensions.
The work of researchers from MIPT was aimed at creating a flexible ferroelectric memory suitable for biomedical applications. Organic polyimide films were chosen as a biocompatible platform, and a 10 nm thick ferroelectric film of zirconium-doped hafnium oxide was chosen as a non-volatile memory material.
Hafnium oxide films exhibit ferroelectric properties, being very thin: from 4 to 30 nanometers, and with other materials, a thickness of more than 100 nanometers is required. Therefore, we expected that the material would be very flexible and would retain its ferroelectric properties under bending and various mechanical deformations."
comments Anastasia Chuprik, Head of the Laboratory of Advanced Concepts of Data Storage at MIPT.
Next, the scientists developed a multi-stage technology for obtaining a flexible biocompatible "flash drive" and a stand for testing mechanical properties. To confirm the results obtained in the experiment, theoretical quantum-mechanical calculations were carried out, which explained the role of mechanical stresses in the ferroelectric properties of film memory.
The technology for obtaining a device on a substrate is very complex and multi-stage. But it made it possible to achieve a very small thickness of the device sample. And to show that the device has unprecedented mechanical properties – it can withstand repeated folding in half – we designed an entire setup. At it, we demonstrated that the device can withstand 150,000 bending cycles and stretching with a load of one and a half kilograms. We would not be able to achieve such figures manually"
says Anastasia Chuprik.
Source: Advanced Electronic Materials
Despite all the tests that the researchers conducted with the film flash drive, it retained its ferroelectric properties.
According to the scientists, they have brought this flexible memory to a sufficiently high level of elaboration, when in a machine for testing mechanical and ferroelectric properties, this flexible film "chip" is simply inserted into a standard connector for reading information.
As a result of the work carried out, it was possible not only to create the device itself with unique mechanical properties. A sophisticated technology for producing thin films with "memory" on a flexible and biocompatible substrate was created, and a stand for testing mechanical and ferroelectric properties was also developed. The device will be able to become a prototype memory for wearable and medical electronics. The technology used and the test bench will help to create new elements of flexible electronics and improve existing storage devices.
The work was carried out with the financial support of the Russian Science Foundation (project No 20-19-00370).

rscf.ru
Number: 20-19-00370
Title: Study of the fundamentals and development of technological processes for the formation of a ferroelectric field transistor for biocompatible flexible electronics
Supervisor: Anastasia A. Chuprik, Ph.D. in Physics and Mathematics
Competition: No45 - Competition 2020 "Conducting fundamental scientific research and exploratory scientific research by individual scientific groups".
..
Annotation
In recent years, flexible electronics have received increasing attention as it offers a number of new applications covering a variety of fields, such as flexible circuits, flexible displays, e-textiles, e-paper, wearables, radio frequency identification (RFID) devices, as well as medical implantable devices. Flexible electronics allow electronic systems to be compact, lightweight, ultra-thin, stretchable, compatible, or even biocompatible.
The next generation of electronics used in biomedical implants requires the development and manufacture of flexible active elements, potentially microcontrollers, including transistors and non-volatile memory for data storage. Non-volatile memory elements must have high integration density, low power consumption, high speed, long service life and uniformity of operating parameters. Several concepts are currently being used to develop flexible non-volatile memory. One of the most attractive is memory based on ferroelectric field effect transistors (FeFET), since it belongs to non-destructive types of non-volatile memory, which significantly increases the resource of devices and simplifies the memory architecture based on them, which, in turn, makes it possible to achieve a high density of memory cells.
Films of polycrystalline hafnium oxide have great potential for creating flexible ferroelectric transistors, since they have ferroelectric properties at a layer thickness of 4-30 nm, which provides low internal mechanical stresses. A flexible ferroelectric transistor based on this material was demonstrated in 2017 using a C60 layer as a channel. The use of C60 and similar materials as channels requires manual manipulation and results in a low yield among prototype devices.
This project is aimed at studying the scientific foundations and developing technological processes for the formation of a flexible biocompatible ferroelectric field-effect transistor based on hafnium oxide as a ferroelectric layer and amorphous hydrogenated silicon a-Si:H as a channel - materials that are processed using well-known technological processes.
In order to study the possibility of creating a flexible ferroelectric transistor with a high state retention time and highly reproducible characteristics, data should be obtained on the effect of surface states at the semiconductor-ferroelectric interface, charged defects in the volume of hafnium oxide and near its interface with electrodes, as well as dead (non-ferroelectric) layers leading to the appearance of built-in fields, on the measured residual polarization of the ferroelectric and, thus, the magnitude of the field effect, as well as its short-term (due to depolarization) and long-term (due to the aging of the ferroelectric) temporal dynamics. Similar answers must be obtained for the influence of mechanical stresses and the direct piezoelectric effect.
Expected results
As a result of the project, prototypes of devices for the element base of flexible biocompatible implantable devices of a new generation should be created - flexible ferroelectric field-effect transistors on a biocompatible platform.
In the course of the project, the following results should be obtained:
1. Technological processes for the formation of flexible ferroelectric capacitors and transistors have been developed.
2. Models of physical mechanisms affecting the operating characteristics of a ferroelectric transistor and their temporal evolution, retention/loss of memory cell state and memory cell resource are constructed.
3. Mechanical stresses in the ferroelectric layer at the working geometry of the devices at different bending angles and planar tensile loads are calculated.
4. Metal-ferroelectric-semiconductor-metal flexible capacitors were manufactured.
5. The evolution of the functional properties (residual polarization, coercive stresses and leakage currents) of ferroelectric capacitors depending on the bending angle, the number of bending cycles, and the value of planar tensile strain is measured.
6. Flexible ferroelectric transistors were manufactured.
7. The evolution of ferroelectric transistor performance is measured as a function of bending angle, number of bending cycles, and planar tensile strain value.
The significance of the expected results is determined by the fact that polycrystalline doped thin-film hafnium oxide and amorphous hydrogenated silicon are materials that are processed using well-known technological processes, which will make it possible to obtain devices with highly reproducible characteristics and high yields. If successful, the results will be a significant contribution to the development of flexible biocompatible implantable devices. The expected results correspond to the world level, they are expected to be published in a series of 8 articles in high-ranking international journals.
Annotation of the results obtained in 2020
This project is aimed at studying the possibility of forming prototypes of ferroelectric transistors on a flexible polyimide substrate with a functional layer of thin-film polycrystalline ferroelectric hafnium oxide to create flexible biocompatible implantable devices. Indeed, the next generation of electronics used in biomedical implants requires the development and implementation of flexible active elements, potentially microcontrollers, including transistors and non-volatile memory for data storage. Non-volatile memory elements must have high integration density, low power consumption, high speed, long service life and uniformity of operating parameters. At the moment, one of the most attractive concepts is the ferroelectric transistor.
..
The tasks of the project are divided into two classes:
1) Study of the scientific foundations of the creation of a ferroelectric transistor on a flexible substrate with a functional layer of thin-film polycrystalline ferroelectric hafnium oxide related to the retention of
The state of the memory cell.
2) Development of technological processes for the creation and testing of prototypes of ferroelectric transistors on a flexible substrate. At the stage of prototyping, we distinguish two directions, depending on the
Semiconductor Electrode Material:
- production of a flexible solar transistor with a graphene channel,
- Production of a flexible SE transistor with a silicon channel.
To test the functional properties of the devices, an appropriate sample design and a bench should be developed that allows electrical measurements to be performed under various mechanical loads.
Publishing
1. Chuprik A.A., Kirtaev R.V., Spiridonov M.V., Markeev A.M., Negrov D.V. Nanoscale Tailoring of Ferroelectricity in a Thin Dielectric Film ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, - (year of publication - 2020)
2. Chuprik A.A., Kondratyuk E.V., Mikheev V.V., Matveev Yu.A., Spiridonov M.V., Chernikova A.G., Kozodaev M.G., Markeev A.M., Zenkevich A.V., Negrov D.V. Origin of the retention loss in ferroelectric Hf0.5Zr0.5O2-based memory devices Acta Materialia, Acta Materialia 204 (2021) 116515 (year of publication - 2021)
"..
Acknowledgements
This work was performed using equipment of MIPT Shared Facilities Center. Device fabrication was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (agreement № 075-00337-20-03, project FSMG-2020-0001). PFM study and capacitance transient measurements were supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Project No. 20-19-00370). HAXPES study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Project No. 18-12-00434)."
Annotation of the results obtained in 2021
At this stage, the following results were obtained:
..
- A technology for manufacturing ferroelectric structures on a flexible polyimide substrate has been developed. Stretchable and ultra-flexible specimens containing functional structures encapsulated in a biocompatible material have been manufactured. The specimens allow for flexural and tensile testing with in situ measurements of electrophysical parameters.
..
- Dependencies of residual polarization, coercive stresses, permittivity, and leakage current on the bending radius and the number of bending cycles (up to 30,000 cycles), as well as the dependencies of the same parameters on the tensile load, have been obtained. It has been established that the manufactured specimens can withstand tensile loads of more than 1 kg, and do not have a critical bending radius, namely, when the specimens are folded in half in the area of working structures, they fully retain their functional properties. Thus, stretchable and ultra-flexible samples of ferroelectric capacitors have been demonstrated, which can be used not only for the development of bioimplants, but also for the development of wearable electronics.
..
- A design has been developed and samples of graphene FeFET with a polyimide sublayer have been manufactured, in which crystallization of HZO into a ferroelectric structural phase is achieved and at the same time a ferroelectric field effect is achieved, which is the maximum possible in CVD graphene at room temperature.
- A method of graphene encapsulation was tested and implemented, which made it possible to achieve the stability of the functional properties of graphene FeFETs.
- Peeling of graphene FeFET samples was performed, in which some of the structures retained their functional properties. Preliminary (ex situ) bending and tensile tests were performed.
Publications:
Local Ga Ion Implantation as a Source of Diverse Ferroelectric Properties of Hafnium Oxide
Elizaveta Guberna, Anastasia Chouprik, Roman Kirtaev, Sergei Zarubin, Ilya Margolin, Maxim Spiridonov, Dmitrii Negrov
First published: 16 October 2021
Abstract
Ferroelectricity patterning in a thin HfO2 film paves a new way for designing innovative switchable photonics devices and microelectronic nonvolatile memory based on hybrid heterostructures of 2D material/ferroelectric (FE) films. For inducing local ferroelectricity, implantation of Ga ions into an amorphous HfO2 film by a pattern is conducted using a focused ion beam followed by rapid thermal annealing. It is demonstrated that the way of Ga implantation as well as the way of annealing play crucial roles in the FE properties of Ga-doped HfO2, including the remnant polarization and the distribution of internal bias fields across the film. Furthermore, the ion implantation in itself is the source of unusual FE properties. The correlation of FE properties with a Fourier analysis of the high-resolution transmission electron microscopy images and results of atomic force microscopy and piezoresponse force microscopy reveals the origin of the observed macroscopical FE performances. It is demonstrated that the ultimate spatial resolution of ferroelectricity patterning is determined by the size of the focused ion beam in the surface plane and thus it reaches 40 nm, which enables new prospects for applications in shortwave active photonics."
[etc. ..]
Annotation of the results obtained in 2022
In 2022, the following results were obtained:
- A model of the effect of charge injection and its capture by traps at the interface with electrodes on the switching rate of storage cells based on HZO was built. It is shown that charge injection, both during the storage of information and during the application of the reading pulse, causes degradation of the switching speed.
- Experimental confirmation of the validity of the model of state loss in structures based on HZO and a method for rapid assessment of state loss, which allows for accurate prediction in record time ("express retention test"), which was proposed at the second stage of the project, was obtained. Added a way to calculate a statistical estimate of state retention time.
..
- The technology for manufacturing flexible ferroelectric transistors with an encapsulated graphene channel has been improved. Prototypes of flexible ferroelectric and non-ferroelectric field-effect transistors with a graphene channel have been manufactured. The dominant role of non-segentoelectric charges and their dynamics on the field effect in graphene in both non-ferroelectric and non-ferroelectric transistors has been revealed.
...
...
Possibility of practical use of the results
The results of the project will contribute to solving the problem of providing domestic developers of silicon and active flexible electronics with the most important type of electronic component base - high-density energy-efficient non-volatile memory of a new generation. This type of memory has the ability to be embedded in systems on a chip, which, in turn, contributes to:
(1) improving the technical and operational characteristics of active flexible electronics through the use of innovative technology,
(2) ensuring the technological independence of the Russian Federation from foreign countries in the field of development and production of the electronic component base of silicon and active flexible electronics,
(3) ensuring the technological priority of the Russian Federation in the development of a new generation of non-volatile memory.
Flexible non-volatile memory applications include flexible displays, e-textiles, e-paper, RFID devices, wearables, medical sensors, and medical implantable devices, including neural implants.
..
Implementation period supported by the RSF: 2020 - 2022, extended to 2023 - 2024. Renewal project card:

rscf.ru
..
In recent years, flexible electronics have received increasing attention as it offers a number of new applications covering a variety of fields, such as flexible circuits, flexible displays, e-textiles, e-paper, wearables, radio frequency identification (RFID) devices, as well as medical implantable devices. Flexible electronics allow electronic systems to be compact, lightweight, ultra-thin, stretchable, compatible, or even biocompatible.
The next generation of electronics used in biomedical implants requires the development and manufacture of flexible active elements, potentially microcontrollers, including transistors and non-volatile memory for data storage. Non-volatile memory elements must have high integration density, low power consumption, high speed, long service life and uniformity of operating parameters. Several concepts are currently being used to develop flexible non-volatile memory.
..
The significance of the expected results is determined by the fact that polycrystalline doped thin-film hafnium oxide and amorphous hydrogenated silicon are materials that are processed using well-known technological processes, which will make it possible to obtain devices with highly reproducible characteristics and high yields. If successful, the results will be a significant contribution to the development of flexible biocompatible implantable devices. The expected results correspond to the world level, they are expected to be published in a series of 8 articles in high-ranking international journals.
The results of the project will contribute to solving the problem of providing domestic developers of silicon and active flexible electronics with the most important type of electronic component base - high-density energy-efficient non-volatile memory of a new generation. This type of memory has the ability to be embedded in systems on a chip, which, in turn, contributes to:
- improving the technical and operational characteristics of active flexible electronics through the use of innovative technology,
- ensuring the technological independence of the Russian Federation from foreign countries in the field of development and production of the electronic component base of silicon and active flexible electronics,
- ensuring technological parity of the Russian Federation in the development of non-volatile memory of a new generation.
Flexible non-volatile memory applications include flexible displays, e-textiles, e-paper, RFID devices, wearables, medical sensors, and medical implantable devices, including neural implants.
..
The development of the new generation of non-volatile high-density ferroelectric memory requires the utilization of ultrathin ferroelectric films. The most promising candidates are polycrystalline-doped HfO2 films because of their perfect compatibility with silicon technology and excellent...

www.mdpi.com
The nanosecond speed of information writing and reading is recognized as one of the main advantages of next-generation non-volatile ferroelectric memory based on hafnium oxide thin films. However, the kinetics of polarization switching in this material have a complex nature, and despite the high...

www.mdpi.com
#^%&%*(^#%$~~!~&(*&^*%$$@











.jpg)

.jpg)













.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)